2 Viet Nam Logistics Infrastructure
The following sections contain information on the logistics infrastructure of Viet Nam.
2.1 Viet Nam Port Assessment
Viet Nam Port Assessment
Vietnam has a 3,200km long coastline with a total of 114 seaports, 14 of which are relatively large and named as the keys to economic development.
However, most ports are relatively small with obsolete facilities and poor supporting services.
The three largest ports of Vietnam are Saigon Port (south), Hai Phong Port (north), and Da Nang Port (central)
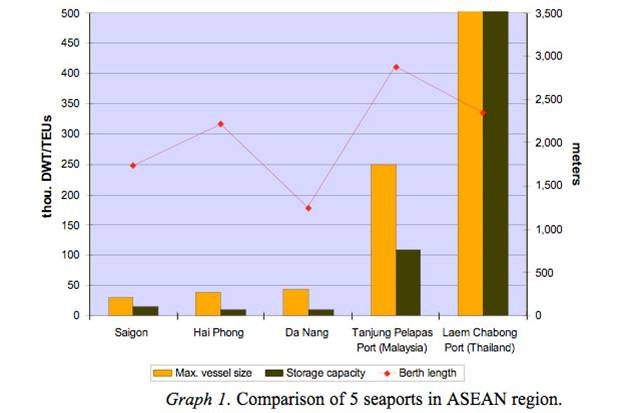
Compare them to some major seaports of Thailand and Malaysia (see graph 1 below). When juxtaposed with them, the three main ports of Vietnam seem diminutive in terms of maximum vessel size allowed and storage capacity in despite the roughly similar size of berth lengths (the figures are for container terminals only; for Thailand, it is 1.2m DWT for maximum vessel size and 4m TEUs storage capacity).
2.1.1 Viet Nam Port of Hai Phong
Key port information can also be found at: Website of the Maritime Database on the Port of Haiphong
Port Overview
The Port of Hai Phong has the highest cargo through-put among the ports in the north of Viet Nam.
The Port is equipped with modern facilities and safe operating practices to accommodate all international modes of transport and trade.
Estimated cargo through-put in the period 2001 – 2003 was 8.5 to 12 million tons per year.
The improvement project at Chua Ve Container Terminal makes the port the biggest and most modern container terminal in the north of Viet Nam with through-put capacity of 500,000 TEU’s per year.
Port website: Website of the Port of Haiphong
|
Port Location and Contacts |
|
|---|---|
|
Country |
Vietnam |
|
Province or District |
Haiphong |
|
Town or City (Closest location) with Distance (km) |
Name: Haiphong km: Haiphong |
|
Port's Complete Name |
n/a |
|
Latitude |
20.86722 |
|
Longitude |
106.68 |
|
Managing Company or Port Authority (If more than one operator, break down by area of operation) |
Vietnam National Shipping Lines |
|
Management Contact Person |
n/a |
|
Closest Airport and Frequent Airlines to / from International Destinations |
Airport Name: n/a Airlines: n/a |
Port Picture
Description and Contacts of Key Companies
4.4 Viet Nam Port and Waterways Company Contact List
Port Performance
It is possible to move freight quickly and efficiently from Hai Phong Port to other world-wide seaports by sea or domestic transport to major economic zones of Viet Nam and the southern provinces of China by road, rail or inland waterway.
|
Handling Figures |
Year 2009 |
|---|---|
|
Vessel Calls |
790,000 |
|
Container Traffic (TEUs) |
n/a |
Total Cargo Handling: 13,800,000 mt
Berthing Specifications
Tug Services – Port of Hai Phong
Ø 8x tug boats ranging in power from 510 – 3,200 HP
Mooring Services – Port of Hai Phong
Ø 6x mooring buoys & 9x anchorage points
Port Handling Equipment
Further information on Port Handling Equipment can be found in the following document:
Vietnam Port of Haiphong Additional Information
Note: The information provided in the attached documents, which has been taken from the old DLCA, does not match the structure of the new LCA and is therefore provided separately.
|
Equipment |
Available (Yes / No) |
Total Quantity and Capacity Available |
Comments on Current Condition and Actual Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Dockside Crane |
n/a |
n/a |
n/a |
|
Container Gantries |
Yes |
6 - 35.6 metres |
n/a |
|
Mobile Cranes |
n/a |
n/a |
n/a |
|
Reachstacker |
n/a |
n/a |
n/a |
|
RoRo Tugmaster (w/ Trailer) |
n/a |
n/a |
n/a |
|
Grain Elevator w/ Bagging Machines |
n/a |
n/a |
n/a |
|
Transtrainer |
n/a |
n/a |
n/a |
|
Forklifts |
Yes |
62 - 3 - 45 mt |
n/a |
Container Facilities
|
Facilities |
20 ft |
40 ft |
|---|---|---|
|
Container Facilities Available |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Container Freight Station (CFS) |
Yes, 2 | Yes |
|
Refrigerated Container Stations |
Yes | Yes |
|
Other Capacity Details |
||
|
Daily Take Off Capacity (Containers per day) |
n/a | |
|
Number of Reefer Stations (connection points) |
n/a | |
|
Emergency Take-off Capacity (Give an indication) |
n/a | |
|
Off take capacity of gang shift (in Containers per shift) |
n/a | n/a |
Port Security
|
Security |
||
|---|---|---|
|
ISPS Compliant (Yes / No) |
Yes |
|
|
Current ISPS Level |
1 |
Level 1 = Normal, Level 2 = Heightened, Level 3 = Exceptional |
|
Police Boats |
n/a | |
|
Fire Engines |
n/a |
2.1.2 Viet Nam Port of Danang
Key port information can also be found at: Website of the Maritime Database on the Port of Danang
Port Overview
Da Nang Port lies at the south end of a bay off the South China Sea in east-central Viet Nam 622 kms north-northeast of Saigon Port in Ho Chi Min City.
Da Nang Port has an excellent harbor enclosed to the east by Tien Sa Peninsula and Cape Da Nang.
Located hear the Da Nang International Airport and the national railroad station, Da Nang Port has easy access to the nation's transportation networks and the hinterland.
In 2008, about 900,000 people lived at Da Nang, one of the country's biggest cities.
In addition to being one of the country's major container ports, Da Nang Port is an industrial city with a fast-growing economy.
The major products produced in the 4,900 factories at Da Nang are seafood, furniture, household goods, and clothing. Tourism is also important to the local economy.
Port website: Website of the Port of Danang
|
Port Location and Contacts |
|
|---|---|
|
Country |
Vietnam |
|
Province or District |
Nadang |
|
Town or City (Closest location) with Distance (km) |
Name: Nadang km: n/a |
|
Port's Complete Name |
n/a |
|
Latitude |
16.2925 |
|
Longitude |
180.3417 |
|
Managing Company or Port Authority (If more than one operator, break down by area of operation) |
Vietnam National Shipping Lines |
|
Management Contact Person |
n/a |
|
Closest Airport and Frequent Airlines to / from International Destinations |
Airport Name: n/a Airlines: n/a |
Description and Contacts of Key Companies
4.4 Viet Nam Port and Waterways Company Contact List
Port Performance
In 2008, Da Nang Port handled a total of 2.7 million tons of cargo, including 1.2 million tons of exports, 525.9 thousand tons of imports, and 985.6 thousand tons of domestic cargo. Cargoes included 61.9 thousand TEUs of containerized cargo. Da Nang Port also served 29.6 thousand passengers in 2008, a significant increase over prior years.
|
Handling Figures |
Year 2009 |
|---|---|
|
Vessel Calls |
61,900 |
|
Container Traffic (TEUs) |
n/a |
Total Cargo Handling: 2.7 million
Berthing Specifications
Tug Services – Port of Da Nang
- Numbers and capacity of tugboats applied in accordance with VINAMARINE ‘s regulations
- Tug assistance charges applied for different type of tugboat when entering, leaving quay or buoy.
- Time of tug service shall be counted from the time the tug leaves the starting position in the port area to take vessel to the place of handling until it returns the starting position or being engaged in another service.
- Minimum time to count tug service: per hour per operation
- General Director shall base on market charge and actual situation to adjust more or less 10% from unit price at point above adjusted cases decided by General Director
- In the event that the port does not have a tug boat and has to supply same from another place: expenses in motivating tug boat shall be determined on the basis of agreement between the tug owner, charterer and the port.
Berthing Equipment Specifications – Port of Da Nang
Wharf: Shore Side
Da Nang Berthing Data: Shore Side Wharf
| Berth #1 | Berth #2 | Berth #3 | Berth #4 | Berth #5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 185m | 185m | 185m | 185m | 225m |
Draft 12m (chart datum)
Size of ship < 45,000DWT and RO-RO ships, container ships 2,000
TEU’s and big and medium sized Passenger ships
Through put: over 4.5 million tons per year
Along with the breaker water of 450 m long facilitates ship
berthing all year round from high waves and monsoon.
Song Han Terminal
Da Nang Berthing Data: Song Han Terminal
| Berth #1 | Berth #2 | Berth #3 | Berth #4 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 140m | 100m | 100m | 90m |
Draft: -0.7m
Accommodation size: 5,000 DWT
Throughput: over 1million per year
Port Handling Equipment
|
Equipment |
Available (Yes / No) |
Total Quantity and Capacity Available |
Comments on Current Condition and Actual Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Dockside Crane |
n/a |
- |
- |
|
Container Gantries |
n/a |
- |
- |
|
Mobile Cranes |
Yes |
23 - 10 to 80 mt |
- |
|
Reachstacker |
n/a |
- |
|
|
RoRo Tugmaster (w/ Trailer) |
n/a |
- |
- |
|
Grain Elevator w/ Bagging Machines |
n/a |
- |
- |
|
Transtrainer |
n/a |
- |
- |
|
Forklifts |
Yes |
32 - 1.5 to 22 mt |
- |
Further information on Port Cargo Handling Equipment can be found in the following document:
Vietnam Port of Danang Additonal Information
Note: The information provided in the attached documents, which has been taken from the old DLCA, does not match the structure of the new LCA and is therefore provided separately.
Container Facilities
|
Facilities |
20 ft |
40 ft |
|---|---|---|
|
Container Facilities Available |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Container Freight Station (CFS) |
Yes | Yes |
|
Refrigerated Container Stations |
Yes | Yes |
|
Other Capacity Details |
||
|
Daily Take Off Capacity (Containers per day) |
n/a | |
|
Number of Reefer Stations (connection points) |
n/a | |
|
Emergency Take-off Capacity (Give an indication) |
n/a | |
|
Off take capacity of gang shift (in Containers per shift) |
n/a | n/a |
Customs Guidance
For information on Viet Nam Port of Danang Customs Guidance, please see the following link:
1.3 Viet Nam Customs Information
Terminal Information
Main Storage Terminal
| Area of Warehouses | Area of Yards | Total Area |
|---|---|---|
| 29,204 m² | 183,722 m² | 299,256 m² |
Port Security
|
Security |
||
|---|---|---|
|
ISPS Compliant (Yes / No) |
Yes |
|
|
Current ISPS Level |
1 |
Level 1 = Normal, Level 2 = Heightened, Level 3 = Exceptional |
|
Police Boats |
n/a | |
|
Fire Engines |
n/a |
2.1.3 Viet Nam Port of Ho Chi Min City
Key port information can also be found at: Website of the Maritime Database on the Port of Ho Chi Min City
Port Overview
The Port of Ho Chi Minh City lies on the Song Sai Gon (Saigon) River about 5 km north-northeast of Saigon Port and about 85 kilometers north of the Mekong River Delta where the river flows into the South China Sea. The Port of Ho Chi Minh City reflects the influence of the French after a century of colonial rule and the United States after almost two decades of war. In 2004, more than 3.4 million people lived at the Port of Ho Chi Minh City. For more information on Ho Chi Minh City, please refer to the Saigon Port link. In 18 years of operation, Saigon Newport Holding Company has developed terminals and operations in the Port of Ho Chi Minh City (or Saigon Newport). The container traffic through the Port of Ho Chi Minh City accounts for over 65% of Ho Chi Minh City's market share and more than 40% of that for the country.
Port website: Website of the Port of Ho Chi Min City
|
Port Location and Contacts |
|
|---|---|
|
Country |
Vietnam |
|
Province or District |
Ho Chi Minh |
|
Town or City (Closest location) with Distance (km) |
Name: Ho Chi Minh City km: n/a |
|
Port's Complete Name |
n/a |
|
Latitude |
10.79389 |
|
Longitude |
106.7247 |
|
Managing Company or Port Authority (If more than one operator, break down by area of operation) |
Saigon Newport Company |
|
Management Contact Person |
n/a |
|
Closest Airport and Frequent Airlines to / from International Destinations |
Airport Name: n/a Airlines: n/a |
Description and Contacts of Key Companies
4.4 Viet Nam Port and Waterways Company Contact List
Port Performance
|
Handling Figures |
Year 2008 |
|---|---|
|
Vessel Calls |
2,168 |
|
Container Traffic (TEUs) |
2,018,104 |
Total Cargo Handling (mt): 25,600,000
Port Handling Equipment
Mooring Services – Port of HCMC
- 3 points of anchorage
|
Equipment |
Available (Yes / No) |
Total Quantity and Capacity Available |
Comments on Current Condition and Actual Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Dockside Crane |
n/a |
- |
- |
|
Container Gantries |
Yes |
3 - 60 to 400 mt |
- |
|
Mobile Cranes |
Yes |
11 |
- |
|
Reachstacker |
Yes |
43 - 42 mt |
- |
|
RoRo Tugmaster (w/ Trailer) |
n/a |
- |
- |
|
Grain Elevator w/ Bagging Machines |
n/a |
- |
- |
|
Transtrainer |
n/a |
- |
- |
|
Forklifts |
Yes |
32 - 28 to 42 mt 22 - 7 to 10 mt |
- |
For further information on operational Port Handling Equipment, please select the following document:
Vietnam Port of Ho Chi Minh City Additional Information
Container Facilities
|
Facilities |
20 ft |
40 ft |
|---|---|---|
|
Container Facilities Available |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Container Freight Station (CFS) |
Yes | Yes |
|
Refrigerated Container Stations |
Yes | Yes |
|
Other Capacity Details |
||
|
Daily Take Off Capacity (Containers per day) |
n/a | |
|
Number of Reefer Stations (connection points) |
1,000 | |
|
Emergency Take-off Capacity (Give an indication) |
n/a | |
|
Off take capacity of gang shift (in Containers per shift) |
n/a | n/a |
Customs Guidance
1.3 Viet Nam Customs Information
Terminal Information
For information on the Tan Cang – Cai Mep Terminal, Tan Cang – Cat Lai Terminal and Tan Cang – Song Than ICD Terminal please select the following document:
Vietnam Port of Ho Chi Minh City Additional Information
Main Storage Terminal
Song Than ICD Terminal
Song Than ICD – Years & Warehouses
| Area of Warehouses | Area of Container Yard | Total Area |
|---|---|---|
| 135,918 m² | 300,000 m² | 500,000 m² |
Port Security
|
Security |
||
|---|---|---|
|
ISPS Compliant (Yes / No) |
Yes |
|
|
Current ISPS Level |
1 |
Level 1 = Normal, Level 2 = Heightened, Level 3 = Exceptional |
|
Police Boats |
n/a | |
|
Fire Engines |
n/a |
2.2 Viet Nam Aviation
Viet Nam Aviation
Key airport information may also be found at:
Website of
Worldaerodata on Vietnam
The Civil Aviation Administration of Viet Nam (CAAV) handles civil aviation and is under direct authority of the government. There are 135 airports and airstrips for civil, military and police use in the country. The CAAV is responsible for 18 airports and air navigation services. The airports in the north, central and south handled 2.5 million, 1.2 million and 5.1 million in 2002, respectively. Air traffic grew sharply during the 1990s until the region was hit by subsequent economic crisis. In 2002, the Ho Chi Minh City (Tan Son Nhat) and Ha Noi (Noi Bai) airports and reached a total of 8 million commercial passengers, of which 4.2 million were international and 3.8 domestic.
International airfares are proposed by the airlines and ratified by CAAV. There are two different domestic airfares: one is applicable to foreign citizens and overseas Vietnamese and other is for local Vietnamese. The maximum airfare to Vietnamese passengers on domestic flights between Ha Noi and Ho Chi Minh City is decided by CAAV and the Government Pricing Committee and approved by the Prime Minister. Two airlines, both members of Viet Nam Airlines Corporation, operate in the country. The dominant one is Viet Nam Airlines, which accounts for 37% of international traffic to and from Viet Nam and 94% of the domestic demand. The other operator is Pacific Airlines which operates mainly between Ha Noi and Ho Chi Minh City. It was established in 1995 and is jointly owned by the Viet Nam Airlines Corporation and several other companies.
2.2.1 Viet Nam Hanoi - Noi Bai International Airport
The airport was originally built for the Vietnamese Air Force use.
After reunification of Viet Nam in 1975 the Ha Noi Noi Bai Airport became an international public airport while continuing to serve for military purposes. Noi Bai International Airport is the largest airport in northern Viet Nam, serves the capital city Ha Noi. Ha Noi Airport is operated by Northern Airport Authority (NAA) and is located 45 kms north of Ha Noi. Travel time by taxi takes between 30 to 45 minutes. Terminal 1 is currently the only passenger terminal in Noi Bai Airport, but there are plans to construct another passenger terminal.
| Location Details | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Country | Vietnam | Latitude | 21.22111 |
| Province / District | Longitude | 105.8072 | |
| Town or City (Closest) | Ha Noi | Elevation (ft and m) | 39 ft / 12 m |
| Airfield Name | Noi Bai International | IATA and ICAO Codes | HAN – VVNB |
| Open From (hours) | 00:00 | Open To (hours) | 24:00 |
Runways
|
Runway #1 |
|
|---|---|
|
Runway Dimensions |
3,200 m x 45 m |
|
Orientation |
11L/29R, 11R/29L |
|
Surface |
Concrete |
Helicopter Pad(s)
|
Helipad #1 |
|
|---|---|
|
Present (Yes / No) |
No |
|
Largest helicopter that can land |
n/a |
|
Width and Length (metres) |
n/a |
|
Surface |
n/a |
Airport Infrastructure Details
|
Customs |
Yes |
JET A-1 fuel |
Yes |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Immigration |
Yes |
AVGAS 100 |
Yes |
|
Terminal Building |
Yes |
Single Point Refueling |
Yes |
|
Passenger Terminal |
Yes |
Air Starter Units |
Yes |
|
Cargo terminal |
Yes |
Ground Power (mobile) |
Yes |
|
Pax transport to airfield |
Yes |
Ground Handling Services |
n/a |
|
Control Tower |
Yes |
Latrine Servicing |
Yes |
|
Weather Facilities |
Yes |
Fire Fighting Category (ICAO) |
Yes |
|
Catering Services |
Yes |
De-icing Equipment |
No |
|
Base Operating Room |
Yes |
Parking Ramp Lighting |
Yes |
|
Airport Radar |
Yes |
Approach & Runway Lights |
Yes |
|
NDB |
Yes |
VOR |
Yes |
|
ILS |
Yes |
|
Companies Available
4.5 Viet Nam Airport Company Contact List
Information on some aviation service providers can be found at:
Website of Azfreight
on Hanoi - Noi Ba International Airport
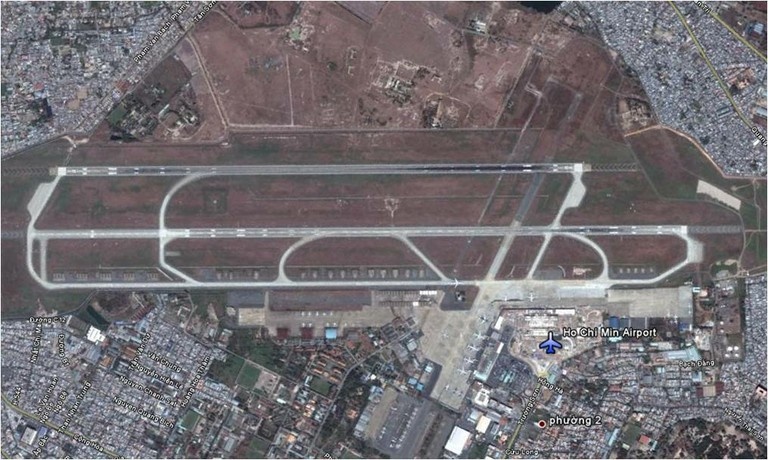
2.2.2 Viet Nam Ho Chi Minh City International Airport
Tan Son Nhat Airport was first constructed in the 1930s by the French Colonial government as small unpaved airport.
By the mid 1950’s USA built a 7,200-foot (2,190 m) runway and terminal facilities to become South Viet Nam's international airport.
During the Viet Nam War, Tan Son Nhut Air Base was used by both the United States and the South Vietnamese Air Force (VNAF).
Ho Chi Minh City Tan Son Nhat International Airport, a joint civilian and military airport, is located 4 miles (6 km) north of the center of Ho Chi Minh City (Saigon).
It operates from two terminal buildings, a Domestic Terminal 1 and International Terminal 2.
The new international terminal opened in September 2007 with the capacity of 10 million passengers per year, giving the airport a total capacity of 15 – 17 million passengers per annum.
| Location Details | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Country | Vietnam | Latitude | 10.81889 |
| Province / District | n/a | Longitude | 106.6519 |
| Town or City (Closest) | Ho Chi Minh | Elevation (ft and m) | 33 ft / 10 m |
| Airfield Name | Tan Son Nhat Airport | IATA and ICAO Codes | SGN – VVTS |
| Open From (hours) | 00:00 | Open To (hours) | 24:00 |
Runways
|
Runway #1 |
|
|---|---|
|
Runway Dimensions |
3,048 m x 45 m |
|
Orientation |
07L/25R |
|
Surface |
Concrete |
|
Runway #2 |
|
|---|---|
|
Runway Dimensions |
3,800 m x 45 m |
|
Orientation |
07R/25L |
|
Surface |
Concrete |
Helicopter Pad(s)
|
Helipad #1 |
|
|---|---|
|
Present (Yes / No) |
Yes |
|
Largest helicopter that can land |
n/a |
|
Width and Length (metres) |
n/a |
|
Surface |
n/a |
Airport Infrastructure Details
|
Customs |
Yes |
JET A-1 fuel |
Yes |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Immigration |
Yes |
AVGAS 100 |
Yes |
|
Terminal Building |
Yes |
Single Point Refueling |
Yes |
|
Passenger Terminal |
Yes |
Air Starter Units |
Yes |
|
Cargo terminal |
Yes |
Ground Power (mobile) |
Yes |
|
Pax transport to airfield |
Yes |
Ground Handling Services |
n/a |
|
Control Tower |
Yes |
Latrine Servicing |
Yes |
|
Weather Facilities |
Yes |
Fire Fighting Category (ICAO) |
Yes |
|
Catering Services |
Yes |
De-icing Equipment |
n/a |
|
Base Operating Room |
Yes |
Parking Ramp Lighting |
Yes |
|
Airport Radar |
Yes |
Approach & Runway Lights |
Yes |
|
NDB |
Yes |
VOR |
Yes |
|
ILS |
Yes |
|
Airport Operating Details
| Operating Details | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum sized aircraft which can be offloaded on bulk cargo: | n/a | ||
| Maximum sized aircraft that can be offloaded on pallet | n/a | ||
| Total aircraft parking area (m²) | n/a | ||
| Storage Area (mt) | n/a | Cubic Meters (m³) | n/a |
| Cargo Handling Equipment Available (Yes / No) | Yes | If "Yes" specify below | |
| Elevators / Hi Loaders (Yes / No) | Yes | Max Capacity (mt) | n/a |
| Can elevators / hi loaders reach the upper level of a B747 (Yes / No) | Yes | ||
| Loading Ramps (Yes / No) | n/a | ||
Security
Security Level: Good
Companies Available
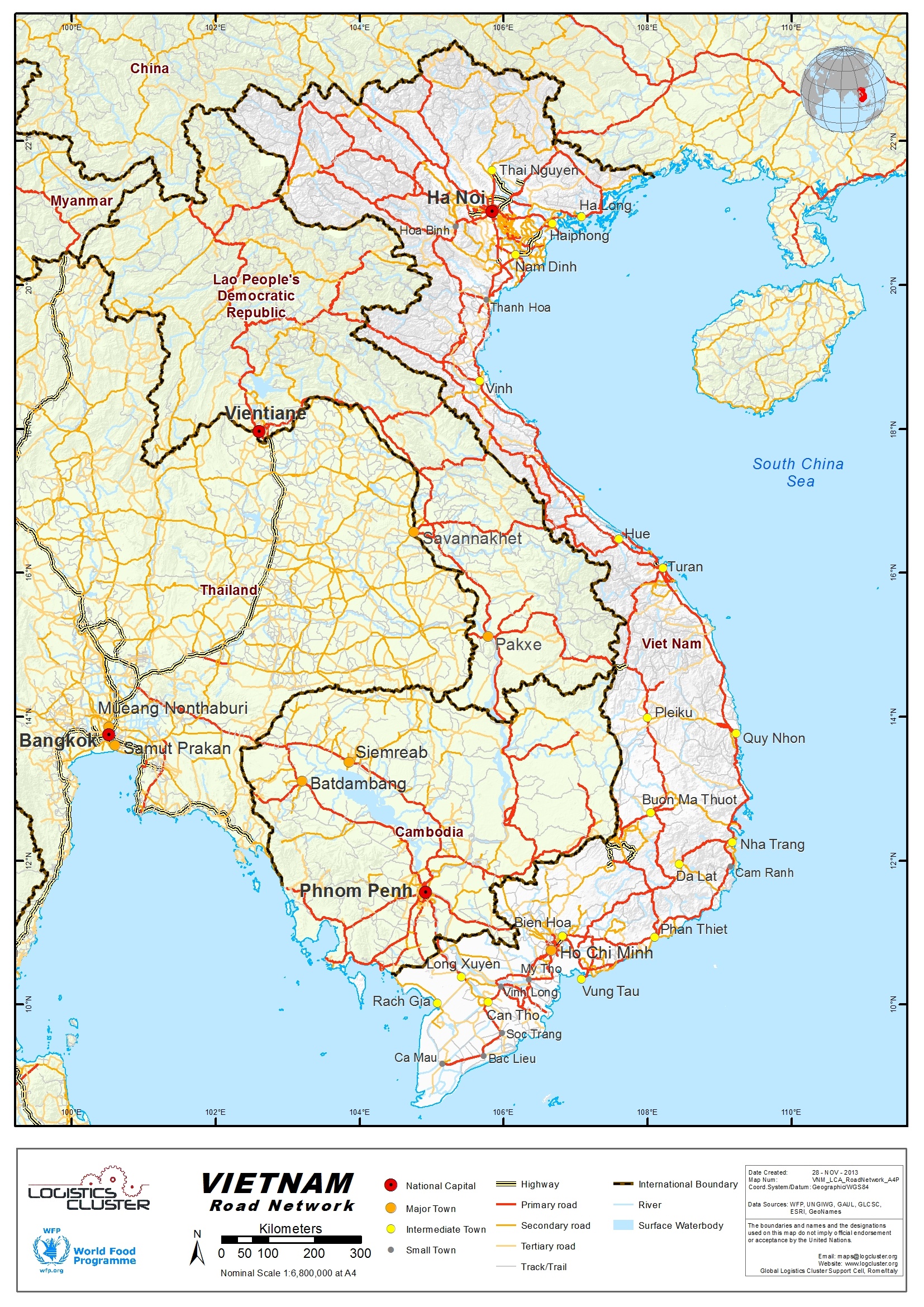
2.3 Viet Nam Road Network
Viet Nam Road Network
Highways
84% of Viet Nam’s national roads are currently paved up from 61%
in 1997. The current percentage of paved national roads is
reasonable by regional standards. In 2002 the condition of the
network in good condition was 45% percent and good and average
66%
The improvement in the quality of the network appears to be largely
driven by new construction rather than by the maintenance of the
existing capital stock because expenditure on periodic and routine
maintenance of national roads between 1998 and 2002 were less than
half the of the maintenance needs as estimated by the Viet Nam
Road's Administration in its 10 Strategic Maintenance Plan.
Local Roads
About one quarter of the 83,000 km rural road network is believed to be in good or fair condition and 58% of the provincial roads providing connectivity to the main network are in poor condition. The administration of the road sector is complex with different agencies responsible for the financing and implementation and others for investment and maintenance.
For national roads, investment finance is approved by the Ministry of Planning and Investment, implementation is the responsibility of the Project Management Units of the Ministry of Transport, and maintenance is undertaken by the Viet Nam Roads Administration with funds channeled through the Ministry of Finance.
Road traffic is mainly concentrated on national roads and around the major urban centers. Even though vehicle ownership is rising very quickly, car ownership is still low and road traffic is dominated by motorcycles. Rising levels of motorization is a major challenge to transport planners and policy-makers, especially in large urban areas and primary intercity roads. Traffic accidents increased dramatically from 1999 to 2002, but have shown a decrease from 2002 to 2003 (See figure 1 below)
4.1 Viet Nam Government Contact List
Further generic information on the road network and the road contacts can be found in the following document:
Vietnam Road Assessment
Additional Information
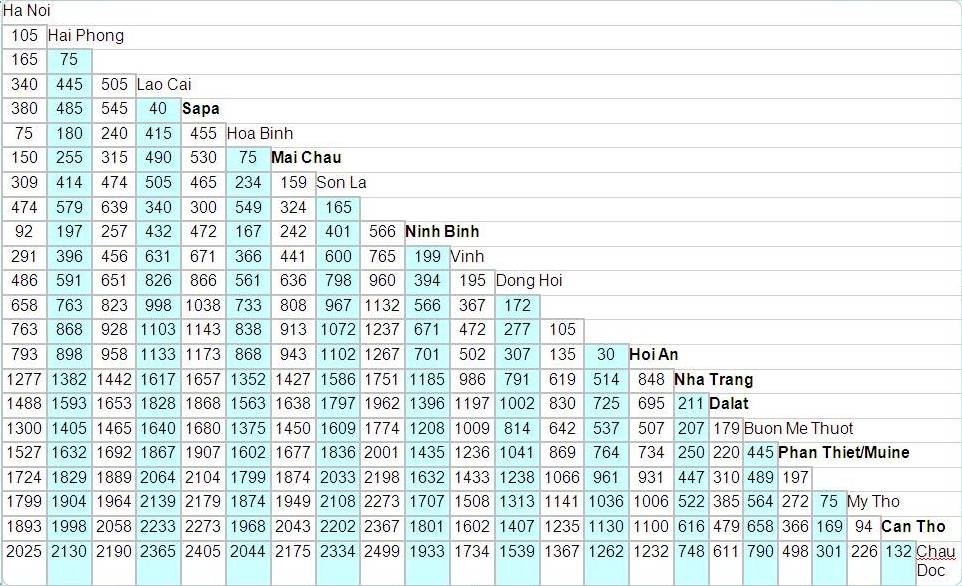
Distance Matrix
Road Class and Surface Conditions
| Classification | Administering Agency | Network Length |
|---|---|---|
|
National Roads
|
-
|
17,300
|
|
Provincial Roads
|
-
|
17,450
|
|
District Roads
|
-
|
36,400
|
|
Urban Roads
|
-
|
7,000
|
|
Rural Roads
|
-
|
131,500
|
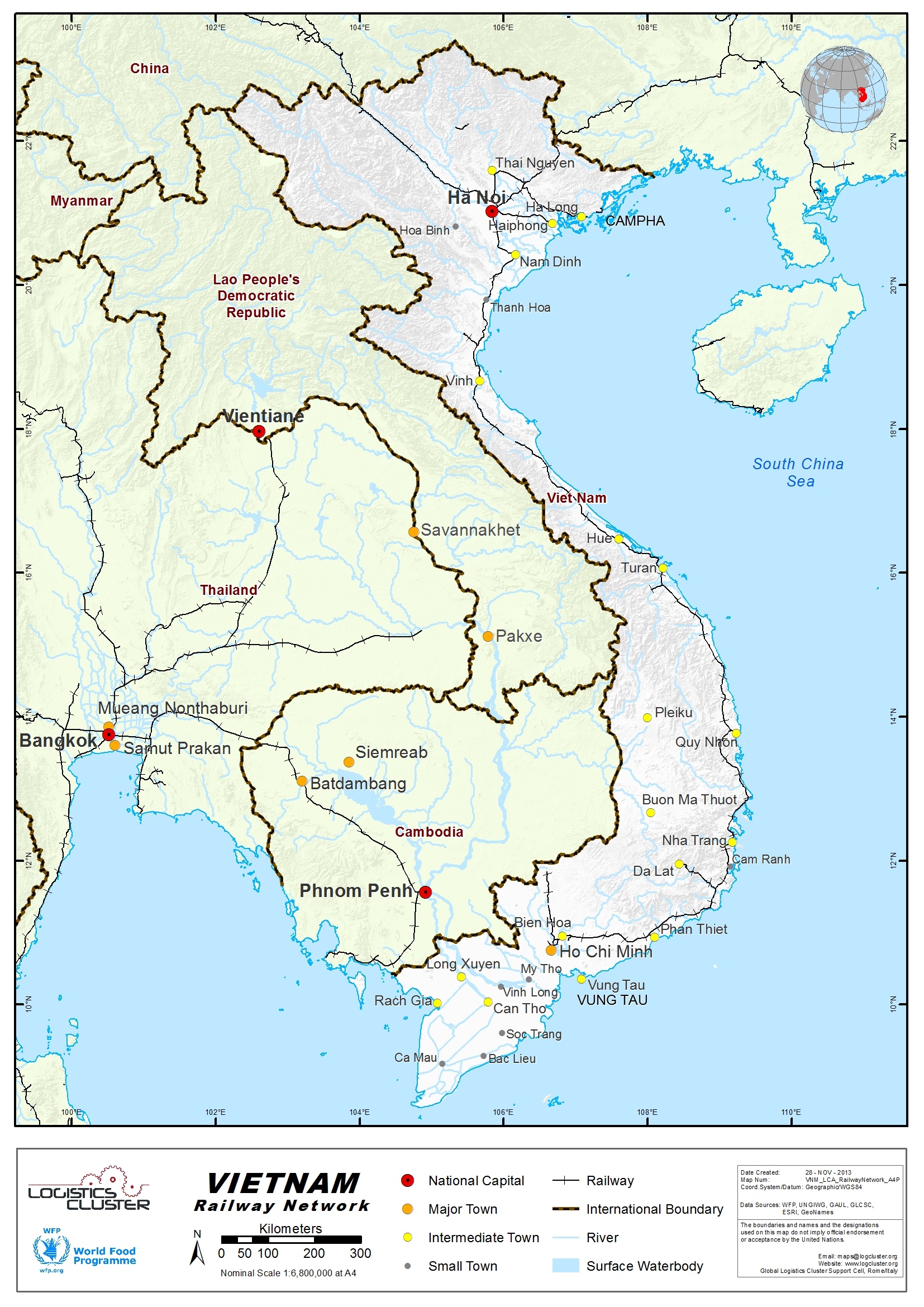
2.4 Viet Nam Railway Assessment
Viet Nam Railway Assessment
The network consists of 7 lines with a total length of 2,600 km.
All lines are single track, mostly meter gauge, with a few standard gauge and double gauge towards the Chinese border.
There are over 1,800 bridges (57,044 m) and 39 tunnels (11,513 m) and 281 stations.
The network connects residential area to cultural, agricultural and industrial center, except the Mekong river delta area.
The railways is linked to China railways according to 2
directions:
o From Lao Cai province to Van Nam province
o From Lang Son province to Quang Tay province
When the network is more developed, the railway could possibly be linked to the Cambodia, Thailand and Malaysia railways network via the Singapore and Laos railways
The Viet Nam railway uses 3 kinds of gauge, namely 1,000 mm gauge, 1,435 mm-gauge (standard gauge) as well as 1,435 mm and 1,000 mm-gauge (mixed gauge). The length of the railway network and gauge are represented in the table next page:
The railways uses twin-block concrete sleeper, wooden sleeper and iron sleeper. 43 kg/m rail type and hard rail fasteners are used in most of the rail network. Some kinds of elastic fasteners are currently used in some divisions.
For additional information on Bridges, Tunnels and Signaling and Telecommunication Systems, please select the following document:
Vietnam Railway Assessment Additional Information
4.1 Viet Nam Government Contact List
Travel Time Matrix
Railway Network Data
| Line | Track Gauge | Track Distance (km) |
|---|---|---|
| Ha Noi – Ho Chi Minh | 1,000 mm | 1,726 |
| Ha Noi – Hai Phong | 1,000 mm | 102 |
| Ha Noi – Lao Cai | 1,000 mm | 296 |
| Ha Noi – Dong Dang | dual gauge (1,435 &1,000 mm) | 163 |
| Ha Noi – Quan Trieu | dual gauge (1,435 &1,000 mm) | 75 |
| Kep – Uong Bi – Ha Long | 1,435 mm | 106 |
| Kep – Luu Xa | 1,435 mm | 57 |
| Total | 3,106 km |
Railway Companies and Consortia
The Viet Nam Railway Cooperation (VRC) is the sole supplier of rail services in Viet Nam.
Following corporatization, VRC’s internal business has been restructured into four main business groups:
- 2 passenger train operating entities (North and South)
- A freight train operating company
- A grouping of regional infrastructure administrations
The train operating entities are quasi-independent management and accounting entities.
The Viet Nam Railway Administration remains responsible for planning development of the sector, for new construction and for securing resources for maintenance.
The VRC pays 10% of its gross revenues as a track access charge.
These funds are generally used toward infrastructure maintenance.
The network is small, old and has received little investment for upgrading, the VRC has performed well.
Viet Nam does not have concentrated flows of bulk raw materials or long-distances which give rise to heavy rail freight flows, its 8 lines serve high density passenger corridors.
Traffic density is about 2.3 million traffic units per route km per annum, which is relatively low compared to other countries in the region.
The average passenger train load in Viet Nam is around 370 passengers which is relatively high, but average freight load of 225 tons is low, as a result of low axle-weight infrastructure, short crossing loops and possible sub-optimal freight operating plans.
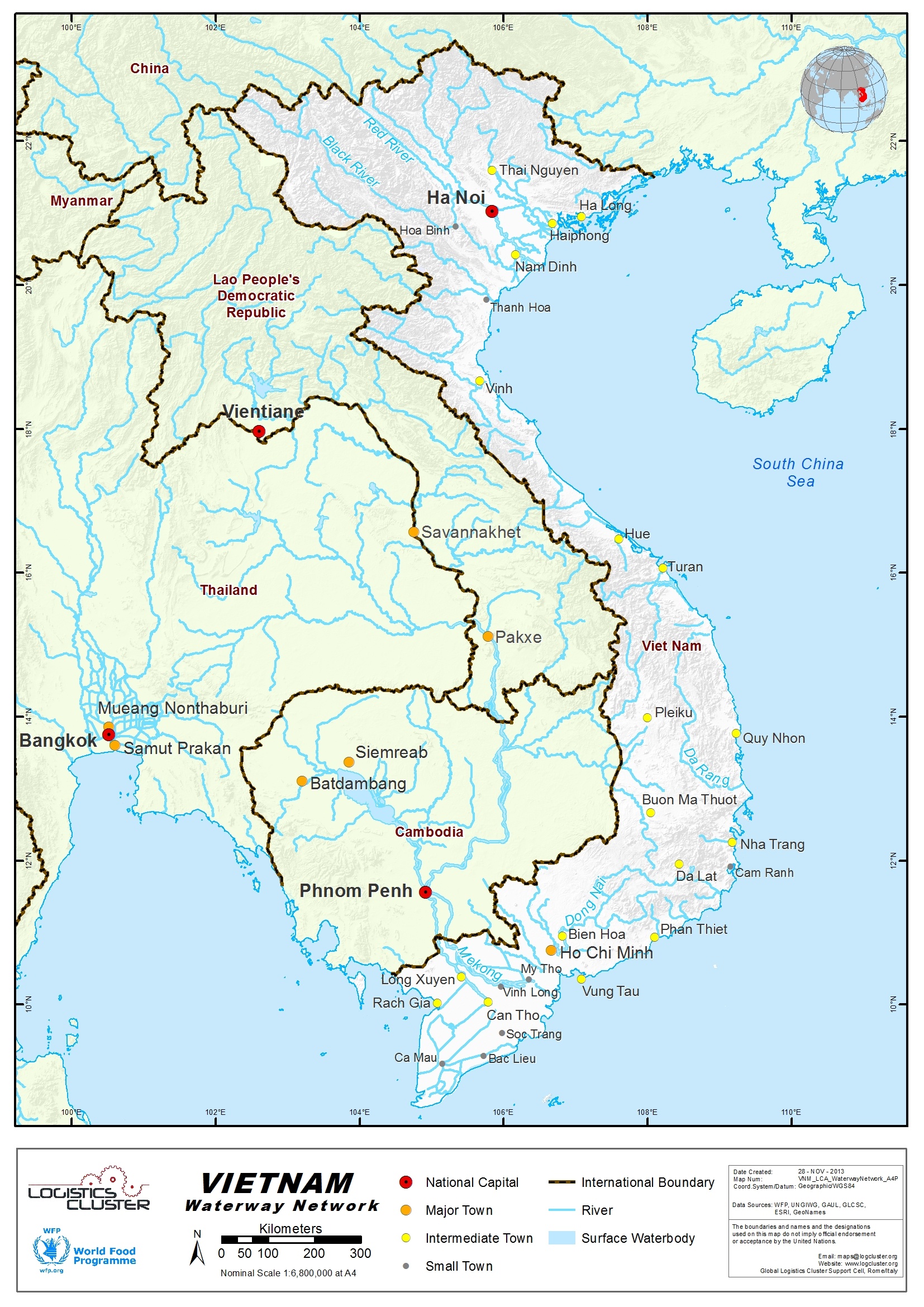
2.5 Viet Nam Waterways Assessment
Viet Nam Waterways Assessment
Mekong Waterways
Viet Nam has 41,000 km of natural waterways, of which 8,000 km are
used commercially.
Of these, the Viet Nam Inland Waterways Administration manages
about 6,000 km as well as the main river ports; local governments
manage the balance of the commercial waterways. River boats and
barges have rapidly developed. In 1999, there were 63,600 units
with a capacity of 1.7 million dead weight tons (DWT) and 197,000
passenger seats.
In 2003 this had increased to 83,000 boats with a capacity of 3.7
million DWT and 280,000 passenger seats. In addition there are tens
of thousands of small “country” boats and ferry boats. Despite
limited investment, the waterways remain attractive for the
transport of coal, rice, sand, stone, gravel, and other usually
high weight low value goods; and livelihoods and personal transport
depend heavily and successfully on waterway transport in the delta
regions of the Mekong and Red River.
The inland waterway system is managed by nine state waterway
management companies; and river ports are managed by three port
authorities. Inland waterway transport services are provided by
state-owned enterprises operating under two state corporations
attached to the Ministry of Transport Northern Waterway Transport
Corporation and Southern Waterway Transport Corporation;
specialized state-owned transport companies under other ministries
carrying materials to cement plants, paper mills and construction
material enterprises, and private for-hire operators.
Private operators have expanded their market share significantly in
recent years. Foreign companies can provide transport services on
the waterways through joint ventures in which the foreigner’s share
does not exceed 49%.
Freight and passenger transport rates are freely determined by
negotiation.
4.1 Viet Nam Government Contact List
For more information on the Waterways Administration contact identified in the contact list above, please select the following document:
Vietnam Waterways Assessment Additional Information
Note: The information provided in the attached documents, which has been taken from the old DLCA, does not match the structure of the new LCA and is therefore provided separately.
Company Information
Transporters
- All the transport companies are regulated or owned by the government.
- Some privately owned fleets have been merged into corporations but the market remains under the control of the government.
4.4 Viet Nam Port and Waterways Company Contact List
Port Information
Ports Activities
The main ports are:
- Saigon
- Bin Thre
- Vinh Long
- Canh Tho
Exported Goods: Mainly rice and coconuts andproducts of the local industry (textile)
Imported Goods: 80% technical equipment for the local industries (agricultural machinery), 20% electronics
Main partner for import and exports: China
Mekong Network Data
Limitations
- Most of the ships’ capacity on the delta ranges from 200 to 400 mt
- Form the sea to Ho Chi Min City, cargo ships of up to 50,000 tons may access the port.
- Then any transport to the inland network is limited to 2,000 mt.
- From the Sea to a distance of about 150 km after Bin Thre / Vinh Long and Canh Tho, the maximum depth is 17 m, and the maximum tonnage for cargo ships is 5,000 mt.
- The rest of the 220 km to Cambodia may be accessed by cargo ships with a maximum of 3,000 mt capacity and the plimsoll line is set to 4 m on the river and its branches.
| Main Type of Boats | |
|---|---|
| Sea Cargo Ships | 2,000 to 5,000 mt, high tonnage (25,000 to 50,000) mt only to HCMC Port |
| Barges | Max 700 mt – sand and other raw building materials |
| Traditional River Transports | Average 300 mt, rice and food transport |
2.6 Viet Nam Milling Assessment
Viet Nam Milling Assessment
For decades Viet Nam struggled to feed itself but is now the
second-largest exporter of rice after Thailand. In 2007, Viet Nam
sold 4.5 million tons to foreign buyers, but the government's
decision to reduce rice exports by 22% caused countries, such as
the Philippines, to urgently secure supplies.
Viet Nam may has a rice surplus, but inflation, an unusually long
winter, pests and diminishing land for rice cultivation, as well as
increasingly frequent and damaging typhoons, are raising concerns
within the government. Improvements in production such as new rice
varieties, better fertilizers, new farm machinery and a reduction
of post-harvest losses have resulted in increased production
Natural Disasters and Adverse Weather
Viet Nam is located in an area where there are frequent typhoons, and sometimes drought, either of which can result in severe crop damage. Fortunately, those areas which suffer most from typhoons are of minor importance in terms of rice production (i.e. the central region, and part of the northern plain). Some areas in the northern plain also suffer from fog, but the damage from this is negligible if properly managed.
Further information on the milling sector in Vietnam can be found by searching the following webpages:
Website of IRIN - provides humanitarian news and analysis
Website of the FFTC - regional information center in the Asian and Pacific Region
Milling Company Chanh Khang Rice Milling
|
Company Name & Address |
Contact Names & Email |
Telephone & Fax |
|---|---|---|
|
Chanh Khang Rice Milling 38-11 Dodclong Street, Tanquy Ward, Tanphu District, Ho Chi Minh City, Viet Nam |
Name: Mr. Phan Thiep Title:Manager Email: ckc@viettel.vn Email: chang_khang@yahoo.com.vn Web: n/a |
Tel: +84 8 3559 0409 Fax: +84 8 6265 8717 |
|
Summary of Role and Services: n/a |
||
Milling Company Viet Nam Flour Industry Co
|
Company Name & Address |
Contact Names & Email |
Telephone & Fax |
|---|---|---|
|
Viet Nam Flour Industry Co Vinh Loc Industrial Park, Lot 32C/I, Street 2G, Ho Chi Minh City, Viet Nam |
Name: n/a Title: n/a Email: n/a |
Tel: n/a Fax: n/a |
|
Summary of Role and Services: n/a |
||
|
Company Name & Address |
Contact Names & Email |
Telephone & Fax |
|---|---|---|
|
Mekong Flour Mill Ltd Floor 2, 28 Phung Khac Khoan St Dakao Ward, District 1, Ho Chi Minh City, Viet Nam |
Name: n/a Title: n/a Email: Mekong@mfml.vnn.vn Web: n/a |
Tel: +84 8 825 7317 Tel: +84 4 825 7318 Fax: +84 8 825 7316 |
|
Summary of Role and Services: n/a |
||