1 Burkina Faso Country Profile
Generic Information
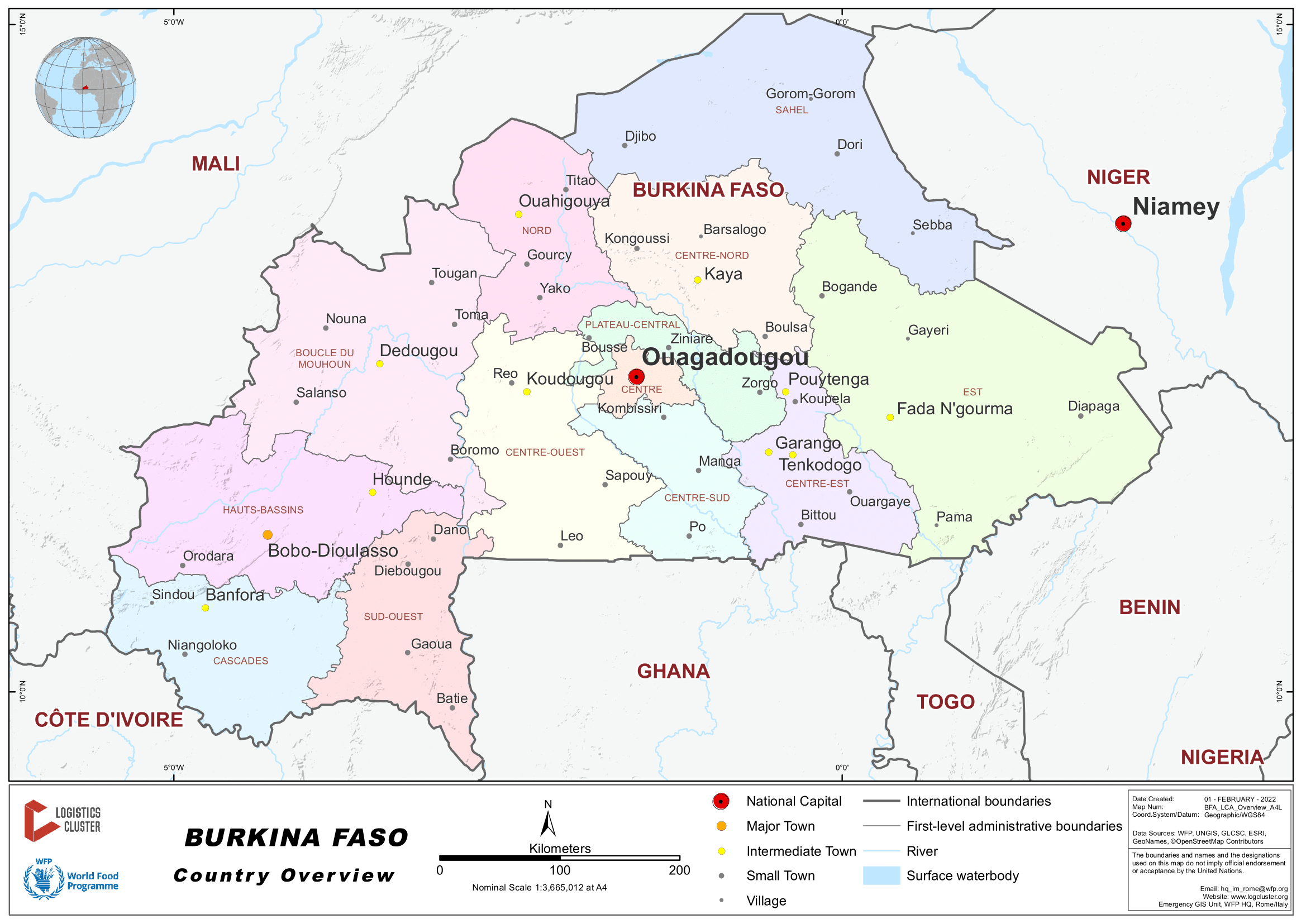
Burkina Faso is a landlocked country in West Africa that covers an area of around 274,200 square kilometres (105,900 sq. mi) and is bordered by Mali to the northwest, Niger to the northeast, Benin to the southeast, Togo and Ghana to the south, and the Ivory Coast to the southwest. The July 2019 population estimate by the United Nations was 20,321,378.
Generic country information can be located from sources which are regularly maintained and reflect current facts and figures. For a generic country overview, please consult the following sources:
Burkina Faso Wikipedia Country Information
Burkina Faso IMF Country Information
Burkina Faso
Economist Intelligence Unit
information*
(*note - this is a paid service)
Humanitarian Info
Burkina Faso World Food Programme Information
Burkina Faso UN Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs Information
Facts and Figures
Burkina Faso Wolfram Alpha Information
Burkina Faso World Bank Information
Burkina Faso World Population Review Information
1.1 Burkina Faso Humanitarian Background
Disasters, Conflicts and Migration
|
Natural Hazards |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
|
Type |
Occurs |
Comments / Details |
|
|
Drought |
Yes |
2.5 million people affected from impact of the climate change. |
|
|
Earthquakes |
No |
N/A |
|
|
Epidemics |
Yes |
Covid 19 epidemic has been active in the country since 2020. As date of 26 July 2021, 13536 confirmed cases, 169 death and 31,671 vaccinated people. For more information, please consult here the WHO Covid 19 Dashboard in Burkina Faso. Malaria is a major health issue in Burkina Faso. It is endemic throughout the country, with a seasonal upsurge from June through October. This seasonal peak is variable across the three major geographic zones linked with the duration of the rainy season: up to three months in the north, six months in the center, and nine months in the south of the country. Dengue is a year-round risk and peak transmission occurs August to December. Cholera case occurs in Burkina Faso with a case detected in August 2021 (the patient was a truck driver of Malian nationality who entered from Niger where a cholera epidemic is currently raging). Although no cases of the Ebola virus disease occurred in Burkina Faso during the West African epidemic of 2014, the Ministry of Health is reinforcing the capacity of its monitoring system to respond in case of a new epidemic. |
|
|
Extreme Temperatures |
No |
The hot season occurs from March to April with an average maximum daily temperature above 38 ° C. |
|
|
Flooding |
Yes |
In September 2020, heavy rains affected central Burkina Faso (particularly the Centre Region, including the area of the capital Ouagadougou, and the Centre-Nord Region), triggering floods that have resulted in casualties and damage (71,341 affected people). |
|
|
Insect Infestation |
Yes |
Migratory locusts. |
|
|
Mudslides |
No |
N/A |
|
|
Volcanic Eruptions |
No |
N/A |
|
|
High Waves / Surges |
No |
N/A |
|
|
Wildfires |
No |
N/A |
|
|
High Winds |
No |
N/A |
|
|
Other Comments |
N/A |
||
|
Man-Made Issues |
|||
|
Civil Strife |
Yes |
|
|
|
International Conflict |
No |
N/A |
|
|
Internally Displaced Persons |
Yes |
As of 30 June 2021, over 1,3 million people had been officially displaced. |
|
|
Refugees Present |
Yes |
22,419 refugees in Burkina Faso as date of August 2021 |
|
|
Landmines / UXO Present |
Yes |
Improvised Explosive Devices (IEDs) are a growing, complex threat in a context already compounded by mass displacement, armed violence and lack of access to basic services. Since 2017, 382 people have been killed or injured in explosive ordnance accidents, all of which were caused by IEDs (98%) |
|
|
Other Comments |
N/A |
||
For a more detailed database on disasters by country, please see the Centre for Research on Epidemiology of Disasters Country Profile.
Seasonal Effects on Logistics Capacities
|
Seasonal Effects on Transport |
||
|---|---|---|
|
Transport Type |
Time Frame |
Comments / Details |
|
Primary Road Transport |
January to January |
The primary road infrastructure is in relatively good condition. |
|
Secondary Road Transport |
June to September |
County roads and rural tracks are not accessible during the rainy season. |
|
Air Transport |
June to September |
Local airfields are not accessible during the rainy season. |
|
Waterway Transport |
Not applicable, the rivers are rarely used for transportation. |
|
In Burkina Faso, the climate is tropical, with a rainy season in the summer months due to the African monsoon (June to September), and a dry season in winter. In the north, the rainy season is shorter and less intense, so the climate is semi-arid, while in the south the rains last longer. The temperatures in Burkina Faso are high throughout the year. During winter season, the air is dry due to the northeast winds with temperatures around 30/32 °C in the north and 32/33 °C in the south. The prevailing wind, called Harmattan, blows from the north-east and can lift dust, making the sky whitish, but it can also cause real sandstorms. Storms can also occur in spring because of the clash with moist air masses.
|
Seasonal Effects on Storage and Handling |
||
|---|---|---|
|
Activity Type |
Time Frame |
Comments / Details |
|
Storage |
June to September |
Hight temperature during summertime which require storage well ventilated and a roof in a good condition to avoid leakage during the rainy season. |
|
Handling |
June to September |
Offloading of trucks outside the warehouse if there is no possibility to park the trucks inside, cargo can be damaged by the rain during the handling operations. |
|
Others |
To remind transporters to protect and cover the shipment with tarpaulins well to avoid damage by the rain. |
|
During the rainy season, offloading of trucks is taking more
time due to the weather conditions and there is a higher risk of
offloading damaged cargo if not well protected and covered at the
departure point. Additional activities of repacking can occur to
replace damaged items during offloading.
Capacity and Contacts for In-Country Emergency Response
Government
Placed under the technical and administrative supervision of the Ministry in charge of Social Action and National Solidarity and under the financial supervision of the Ministry in charge of the Economy and Finance, the Conseil National de Secours d’Urgence et de Réhabilitation (CONASUR) is responsible for working to prevent disasters, manage emergency relief and rehabilitation and ensures coordination and guidance in the field of prevention disaster, emergency relief management and rehabilitation. The CONASUR is the national platform for the prevention and management of disasters and humanitarian crises with the aim to work in closed collaboration with all humanitarian actors, on issues related to the convergence of actions for poverty reduction, adaptation to climate change and disaster risk reduction, to strengthening the resilience of populations made vulnerable by socio-political-economic systems and climate change including climate variability and extreme events.
Additional governmental agencies are interacting within the humanitarian action in country such as:
- The Société nationale de gestion des stocks de sécurité alimentaire (SONAGESS) is in charge of managing the national food stock security.
- SP-PAM in charge of the administration, management, monitoring-evaluation and control of food aid from the World Food Programme (WFP).
For more information on government contact details, please see the
following link: 4.1
Government Contact List.
Humanitarian Community
As of April 2021, 67 organizations were operating
in the country implementing 157 (shelter, wash,
protection, nutrition, health, food security, refugees).
As per an OCHA report issued on 26/07/21, the number of internally
displaced persons in Burkina Faso has risen to 1,312,071. This
increase in numbers is due to the increase in security incidents.
This unpredictable and unprecedented increase in incidents
targeting the civilian population has been observed since the
beginning of the second quarter of 2021 (…) The Central North,
Sahel and Eastern regions continue to be the most affected. People
are moving to communities in dire humanitarian need, but
humanitarian response capacity remains limited. According to
analyses by the Rapid Response Coordination Group (GCORR), only 20%
of displacement alerts are fully responded to. The humanitarian
community remains committed to supporting the Government in
responding to humanitarian challenges.
For more information on humanitarian agency contact details, please see the following link: 4.2 Humanitarian Agencies Contact List.
1.2 Burkina Faso Regulatory Departments and Quality Control
Regional Organizations and Trade Agreements
Burkina Faso is a member of WTO (since 1995), GATT (since 1963) including the below organizations:
- Economic Comission of West African States (ECOWAS): this organization aims to promote cooperation and integration. It aims to establish an economic union in west Africa to raise the living standards of its peoples, and to maintain and enhance economic stability, foster relations among member states, and contribute to the progress and development of the African continent.
- West African Economic and Monetary Union (WAEMU).
- ISO: the Agence Burkinabè de Normalisation, de la Métrologie et de la qualité (ABNORM) is responsible for developing standards. One of ABNORM’s key objectives is to cover all Burkina Faso’s priority sectors for standardization (food, electro-technical, environmental, building and civil engineering sectors).
Regulatory Agencies
Burkina Faso has numerous regulatory bodies to set standards of the economy and then to enforce those standards:
Pharmaceutical
The Agence Nationale de la Régulation Pharmaceutique (ANRP), the main objectives are to guarantee access to quality, safe, effective and accessible health products for the entire population.
Telecommunication
The Autorité de Régulation des Communications Electroniques et des Postes(ARCEP) the main missions are to monitor compliance with regulations and commitments made by network operators and service providers, internet DNS domain management, approval of imported/local made electronic equipment or radio frequencies management.
Energy
Autorité de Régulation du Sous-secteur de l’Electricité (ARSE) a public establishment under to the Ministry of Energy with the aim to contribute to the proper functioning of the electricity sector through the regulation of production, operation, transport, distribution, sale, export and import activities of electricity throughout of the national territory.
Fuel
The Comité Interministériel de Détermination des Prix des Hydrocarbures (CIDPH) is a decision-making support structure that the government has set up to make relevant proposals to determine the price of hydrocarbons month after month in country.
Civil Aviation Authority
The Agence Nationale de l’Aviation Civile (ANAC) in charge of the regulation, supervision and control of civil aviation activities in country.
Laboratory and Quality Testing Companies
Laboratoire National de Santé Publique (LNSP)
LNSP is a public establishment under to the Ministry of Health responsible for the quality control of health products, food, water and beverages pesticides, cosmetics, tobacco, and cigarettes (and all other products and articles likely to constitute threats to health). LNSP controls are followed by the issuance of a sanitary quality certificate.
Institut de Recherche en Science Appliquée et Technologie/ Département de Technologie Alimentaire (IRSAT/DTA)
- Research & development in food and nutritional sector
- Food quality control
- Supporting the Agri-food industry development
- Technology and skills transfer
- Promotion of equipment and processes in the food industry
Consulting support for the implementation of the quality
approach
Laboratoires des Universités publiques du Burkina (UJKZ, UNB)
- Initial training and research in the food and nutritional sector
- Food quality Control
- Consulting support for the implementation of the quality approach
Agence National de Biosécurité (ANB)
- GMOs Quality Control
Laboratoire National de l’Elevage (LNE)
- Food Quality control of animal origin
- Search for chemical residues in food of animal origin
- Control of the microbiological quality of animal feed
- Conducting research in the field of food safety
- Zoonotic disease surveillance
- Training of farmed technicians
Public and governmental laboratories
- ONEA (Office National de l’Eau et de l’Assainissement)
- SONABEL (Société Nationale d’Electricité du Burkina)
- Private structures
- AINA Laboratories: perform physiochemical and bacteriological analyzes, water sanitation.
Inspection Companies
Local companies like Groupe CEM or Tecal-Sate are assisting in quality control through food testing at vendor’s location prior delivery at customer ‘s warehouse. Their agents called “superintendent” are collecting samples to run laboratory analysis then provide advice according to the lab results. They also monitor loading and/or unloading operations by checking weight and visual aspect of the goods. International companies like Bureau Veritas and SGS are also operating in country and offer an extensive range of services from testing (bacteriological and chemical sampling analyses and quality analyses of submitted samples) inspection (supervision of loading and discharging), audit and certifications.
Pre-shipment Inspection
From September 2018 there is no longer a requirement for pre-shipment inspection to enable goods to be imported into Burkina Faso.
For more information on regulatory departments and quality control laboratories’ contact details, please see the following links: 4.1 Government Contact List and 4.3 Laboratory and Quality Testing Company Contact List.
1.3 Burkina Faso Customs Information
Duties and Tax Exemption
For contact information regarding government custom authorities, please follow the link below: 4.1 Government Contact List.
Emergency Response
|
Agreements / Conventions Description |
Ratified by Country? |
|---|---|
|
WCO (World Customs Organization) member |
Yes, since September 1966 |
|
Annex J-5 Revised Kyoto Convention |
Yes, since July 8, 2017 |
|
OCHA Model Agreement |
No |
|
Tampere Convention (on the Provision of Telecommunication Resources for Disaster Mitigation and Relief Operations) |
No |
|
Regional Agreements (on emergency/disaster response, but also customs unions, regional integration) |
Projet MADAO (projet de modernisation des administrations
douanières d’Afrique de l’Ouest). |
Exemption Regular Regime (Non-Emergency Response)
United Nation Agencies and NGOs are defined in fiscal terms as non-profit organizations participating in the implementation of the development aid of the Government. Indeed, as they are performing public service missions normally under to the State, they benefit from certain favors on their investment made for the benefit of the populations. As a result, in accordance with the Establishment Convention signed with the DGCOOP, UN agencies and NGO are exempted from taxes, duties and customs duties for the purchase of goods and services necessary for activities carried out for the benefit of the populations. However, any profitable activities are excluded.
- Tax exemption is based on article 31 of the agreement establishment signed between the Government and UN agencies/NGO in Burkina Faso. They are exempted of the VTA in accordance with the Letter #2055/ MEF/ 25/11/1996, law #06-2010 dated on January 29, 2010.
- Customs duties exemption is based on article 30 of the agreement establishment signed between the Government and UN agencies/NGO.
|
Organizational Requirements to obtain Duty Free Status |
|---|
|
United Nations Agencies |
|
UN agencies must submit an official letter to the Director of
DGD to obtain a
customs exemption of duty and taxes (also applicable for temporary
import IT and temporary admission AT)
|
|
Non-Governmental Organizations |
|
NGO must submit an official letter to the Director of DGD to
obtain a customs exemption of duty and taxes, a temporary import
(IT) and/or a temporary admission (AT)
|
Exemption Certificate Application
Procedure
|
Duties and Taxes Exemption Application Procedure |
|---|
|
Generalities (include a list of necessary documentation) |
|
VAT Refund / DGI
|
|
Process to be followed (step by step or flowchart) |
|
VAT exemption form to be submitted to the Secretary of DGI then proceeded within seven working days. The VAT exemption certificate is issued for a maximum period of one year regardless of the number of years of the exemptions granted. |
Exemption Certificate Document
Requirements
|
Duties and Taxes Exemption Certificate Document Requirements (by commodity) |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
Food |
NFI (Shelter, WASH, Education) |
Medicines |
Vehicle & Spare Parts |
Staff & Office Supplies |
Telecoms Equipment |
|
Exoneration Certificate (EXO) |
Yes, Original and 1 copy, |
Yes, Original and 1 copy, |
Yes, Original and 1 copy, |
Yes, Original and 1 copy, |
Yes, Original and 1 copy, |
Yes, Original and 1 copy, |
|
Invoice |
Yes, Original and 4 copies, |
Yes, Original and 4 copies, |
Yes, Original and 4 copies, |
Yes, Original and 4 copies, |
Yes, Original and 4 copies, |
Yes, Original and 4 copies, |
|
AWB/BL/Other Transport Documents |
Yes, Original and 1 copy, |
Yes, Original and 1 copy, |
Yes, Original and 1 copy, |
Yes, Original and 1 copy, |
Yes, Original and 1 copy, |
Yes, Original and 1 copy, |
|
Donation/Non-Commercial Certificates |
Yes, Original and 1 copy, |
Yes, Original and 1 copy, |
Yes, Original and 1 copy, |
Yes, Original and 1 copy, |
Yes, Original and 1 copy, |
Yes, Original and 1 copy, |
|
Packing Lists |
Yes, Original and 1 copy, |
Yes, Original and 1 copy, |
Yes, Original and 1 copy, |
Yes, Original and 1 copy, |
Yes, Original and 1 copy, |
Yes, Original and 1 copy, |
|
Other Documents |
n/a |
n/a |
n/a |
n/a |
n/a |
n/a |
Customs Clearance
General Information
|
Customs Information |
|
|---|---|
|
Document Requirements |
Any customs clearance procedure must be handled by an official
and registered Authorized Customs Agent only. The following documents are required for customs formalities and are issued through the SYLVIE electronic platform since 2016 (virtual liaison system for import and export transactions):
The clearance system incorporates a four-channel risk management system: green (good for release), blue (a posteriori control), yellow (inspection of documents) and red (full-scale physical inspection of the goods). |
|
Embargoes |
None |
|
Prohibited Items |
|
|
General Restrictions (Products subject to special import authorization) |
|
| Specific restrictions (product subject to special export authorization) |
Cereals (mil, corn, cowpea, sorghum). However, since 1stJanuary 2021, ASE (Autorisation Spéciale d’Exportation) has been suspended by the government until further notice (MICA communication dated in July 2021 available here). |
Customs Clearance Document Requirements
|
Customs Clearance Document Requirements (by commodity) |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
Food |
NFI (Shelter, WASH, Education) |
Medicines |
Vehicles & Spare Parts |
Staff & Office Supplies |
Telecoms Equipment |
|
Exoneration Certificate (EXO) |
Yes, Original and 1 copy, |
Yes, Original and 1 copy, |
Yes, Original and 1 copy, |
Yes, Original and 1 copy, |
Yes, Original and 1 copy, |
Yes, Original and 1 copy, |
|
Invoice |
Yes, Original and 4 copies, |
Yes, Original and 4 copies, |
Yes, Original and 4 copies, |
Yes, Original and 4 copies, |
Yes, Original and 4 copies, |
Yes, Original and 4 copies, |
|
AWB/BL/Other Transport Documents |
Yes, Original, 1 copy, |
Yes, Original, 1 copy, |
Yes, Original, 1 copy, |
Yes, Original, 1 copy, |
Yes, Original, 1 copy, |
Yes, Original, 1 copy, |
|
Donation/Non-Commercial Certificates |
Yes, Original and 1 copy, |
Yes, Original and 1 copy, |
Yes, Original and 1 copy, |
Yes, Original and 1 copy, |
Yes, Original and 1 copy, |
Yes, Original and 1 copy, |
|
Packing Lists |
Yes, Original and 1 copy, |
Yes, Original and 1 copy, |
Yes, Original and 1 copy, |
Yes, Original and 1 copy, |
Yes, Original and 1 copy, |
Yes, Original and 1 copy, |
|
Phytosanitary Certificate |
Yes, Original and 1 copy, |
n/a |
n/a |
n/a |
n/a |
n/a |
|
Other Documents |
|
n/a |
ASI from Ministry of Trade and Authorization from ANRP to import. |
For vehicle only: Certificate of conformity & Certificate of value. |
n/a |
n/a |
|
Additional Notes |
||||||
|
ASI means “Autorisation Spéciale d’Importation,” please go to PEB website for further information. |
||||||
Transit Regime
During international transit in Burkina, the authorized customs agent delegated for this operation must fill and obtain a IM8 form called “Déclaration de Transit” at the entry border. Once obtained, the Customs release the cargo then date of departure is recorded within their system. A grace period from 48 to 96 hours is granted to the transporter to reach the exit border with an escort appointed during the journey (cost is 15 000 FCFA). In case of accident or breakdown, the transporter must inform immediately the escort or any relevant local authority otherwise a fine will be applied at the exit border. Escort is only applicable for sensitive/high value cargo (pharmaceuticals, arms, oil. etc).