1 Cambodia Country Profile
Generic Information
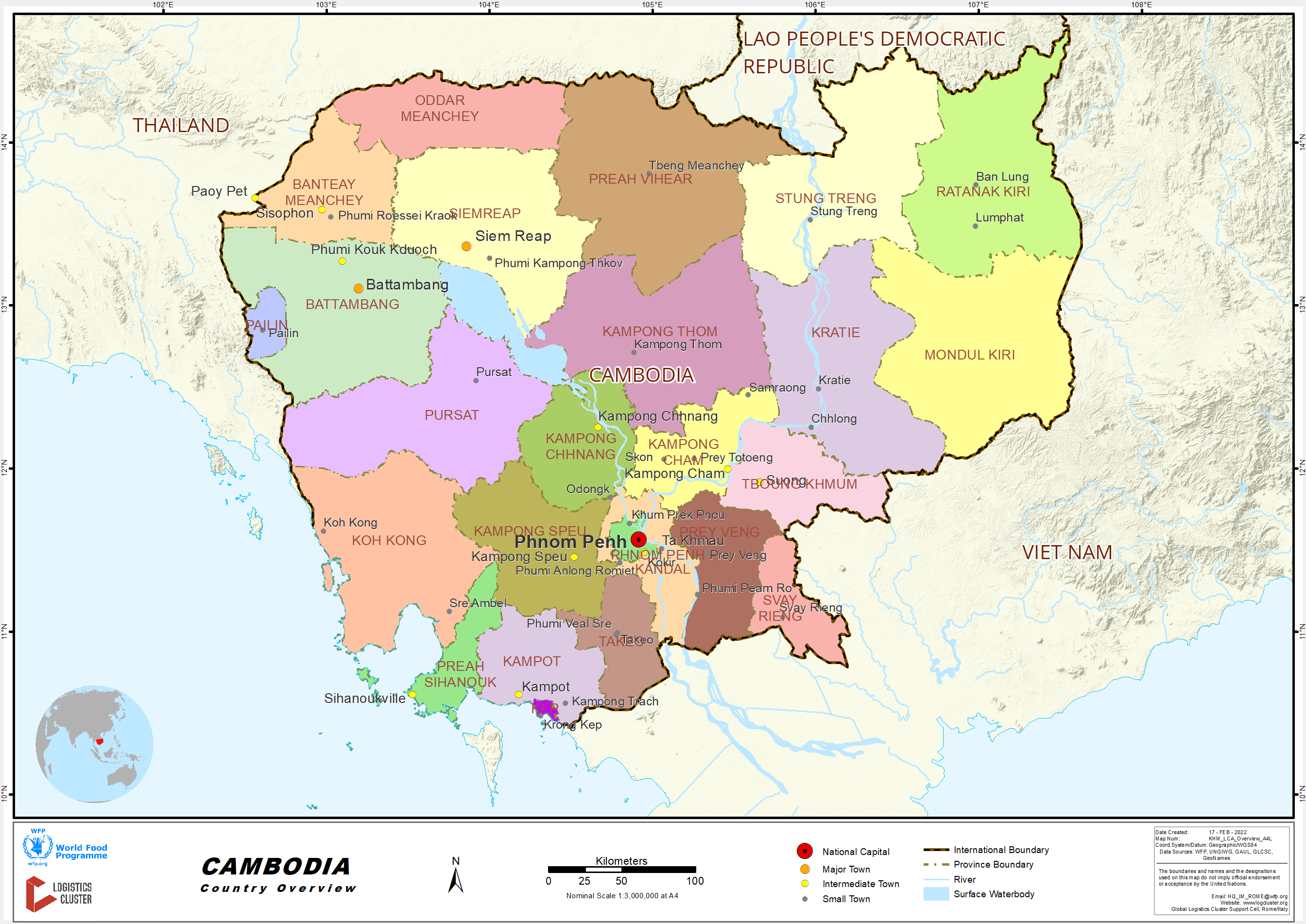
The Kingdom of Cambodia, formerly Kampuchea, is a Southeast Asian nation that borders Thailand, Laos, Vietnam, and the Gulf of Thailand. The capital city is Phnom Penh.
Geography
Situated in the southwest of the Indochinese peninsula, Cambodia occupies a total area of 181,035 km2 and borders Thailand to the west and northwest, Laos to the northeast, Vietnam to the east, and Gulf of Thailand to the southwest. Cambodia’s geographic coordinates are 13 00 N, 105 00 E. Cambodia’s terrain consists mainly of low plains, with mountains to the southwest and north. Two dominant physical features of Cambodia are the Mekong river, which runs from north to south of the country, and the Tonlé Sap Lake. Natural resources include oil and gas, timber, gemstones, iron ore, manganese, phosphates, hydropower potential.
Population
Cambodia’s population is approximately 16.9 million. 90 percent of residents are Khmer. The rest are Cham (Khmer Muslim), Chinese, Vietnamese, Indian, Thai, Phnorng, Kuoy, Stieng, Tamil, etc. The Population density is 78/km.
Climate
Like most of Southeast Asia, Cambodia’s climate is hot and warm almost all year round. The climate is dominated by the annual monsoon cycle of rainy and dry seasons. The rainy season lasts from May to October, and the dry season from November to April. December to January are the coolest months, while the hottest period is in April. The average temperature is around 27-28ºC.
Source: Ministry of Tourism, http://www.tourismcambodia.org/contents/about_cambodia/#comp
For a generic country overview, please consult the following sources:
Economist Intelligence Unit Information on Cambodia*
(*note - this is a paid service)
Wikipedia Information on Cambodia
Humanitarian Info
World Food Programme Information on Cambodia
Facts and Figures
Wolframalpha Information on Cambodia
World Bank Information on Cambodia
1.1 Cambodia Humanitarian Background
Disasters, Conflicts and Migration
|
Natural Hazards |
||
|---|---|---|
|
Type |
Occurs |
Comments / Details |
|
Drought |
Yes |
During dry season from Dec to Apr |
|
Earthquakes |
N/A | |
|
Epidemics* |
Yes |
Malaria (Objective: elimination by 2030), Influenza, Tuberculosis and HIV/AIDS. Chikungunya (2020 Outbreak). Dengue outbreaks occur each rainy season (May–October) |
|
Extreme Temperatures |
N/A | |
|
Flooding |
Yes |
During monsoon from May to Nov |
|
Insect Infestation |
N/A | |
|
Mudslides |
N/A | |
|
Volcanic Eruptions |
N/A | |
|
High Waves / Surges |
N/A | |
|
Wildfires |
N/A | |
|
High Winds |
Yes |
June to August and Nov to March |
|
Other Comments |
Cambodia is highly vulnerable to hydro-meteorological hazards, including flash floods, riverine floods and tropical cyclones/storms, with regular monsoon flooding in the Mekong and Tonle Sap basin with localised increasing droughts in the plains. The changing climactic pattern brings enormous implications for agriculture and fisheries, with the potential to threaten food and water security. Riverbank and constructions collapses, fires as well as epidemics are also disasters threats. |
|
|
Man-Made Issues |
||
|
Civil Strife |
Yes |
Likely during past election years. |
|
International Conflict |
Yes |
Last happened in 2010/11 due to boundaries dispute with Thailand. Civil war ended in 1993. |
|
Internally Displaced Persons |
Yes |
Can occur during severe floods. Return migrants from Thailand following Covid-19 outbreak |
|
Refugees Present |
No |
Happened during the civil war until 1993. |
|
Landmines / UXO Present |
Yes |
Cambodia has one of largest landmine and explosive remnants of war (ERW) contaminations in the world (Objective: Clear EWR by 2030*). Mainly located in north-eastern rural areas and a high concern at flood’s time. |
|
Other Comments |
The Kingdom is looking closely at China and Laos' extensive upstream dam construction and member of the Mekong River Commission (MRC). |
|
For a more detailed database on disasters by country, please see the Centre for Research on Epidemiology of Disasters Country Profile
Seasonal Effects on Logistics Capacities
|
Seasonal Effects on Transport |
||
|---|---|---|
|
Transport Type |
Time Frame |
Comments / Details |
|
Primary Road Transport |
May to Nov |
There are normally no major consequences to primary road transport, except under heavy rainfall or river flooding some part of the main roads could be cut by water. |
|
Secondary Road Transport |
May to Nov |
There are more effects to Secondary road transport, although infrastructure conditions have much improved. |
|
Rail Transport |
- |
Rail transport is newly developed in Cambodia. There have been no noticeable seasonal effects although the railway operator is looking at it closely and taking necessary preventive measures to prevent potential disruption due to flood. |
|
Air Transport |
May to Nov |
Limited seasonal effects, although heavy rains and strong winds can delay flights. |
|
Waterway Transport |
Jan to May |
In rainy season there is no major problem with boat transport, but in the dry season some part of the water line cannot be reached due to shallow river levels. |
Cambodia's climate, like that of the rest of Southeast Asia, is dominated by monsoons, which are known as tropical wet and dry because of the distinctly marked seasonal differences.
Cambodia has a temperature range from 21 to 35 °C (69.8 to 95.0 °F) and experiences tropical monsoons. Southwest monsoons blow inland bringing moisture-laden winds from the Gulf of Thailand and Indian Ocean from May to October. The northeast monsoon ushers in the dry season, which lasts from November to April. The country experiences the heaviest precipitation in October with the driest period occurring in February.
In 2020, there has been major disruption in transport network during the rainy seasons, exceptional floods and flash floods disrupted the normal traffic circulation for several hours up to few days.
|
Seasonal Effects on Storage and Handling |
||
|---|---|---|
|
Activity Type |
Time Frame |
Comments / Details |
|
Storage |
Jan to Dec |
No seasonal effects on storage. |
|
Handling |
Jan to Dec |
In Provinces, handling remain mainly done by manpower and currently strongly affected by migration to neighbouring countries for work. |
|
Other |
N/A |
Forklift may not always be available and truck cranes are used instead. |
Capacity and Contacts for In-Country Emergency Response
Government
The 2015 Disaster Management law outlines the Government’s response to emergencies, with National Committee for Disaster Management (http://www.ncdm.gov.kh) and its subnational committees responsible for coordination at the national and subnational levels respectively.
In 2020, the Circular No. 02 [Khmer Abbreviation] dated 14 January 2020, set the establishment of mechanism for disaster management in ministries and institutions of the Royal Government of Cambodia and the Letter No. 014 [Khmer Abbreviation] dated 17 January 2020, set the establishment of Disaster Management Secretariat of the NCDM in ministries and institutions.
In support of the government, the Cambodian Red Cross provides the first assistance and draw on a wide network of pre-positioned resources and subnational presence. (http://www.redcross.org.kh)
For more information on government contact details, please see the following link: 4.1 Government Contact List.
Humanitarian Community
The Humanitarian Response Forum (HRF), created in 2011, is the coordination mechanism used by the humanitarian community to address emergency preparedness and responses, information management and resource mapping in an efficient and coordinated approach and close collaboration with NCDM. The HRF is currently co-chaired by WFP and Dan Church Aid.
It is organised in 6 sectors: Food Security and Nutrition, Water Sanitation and Hygiene, Shelter, Health, Education, Protection. The creation of 2 working group “Cash” and “Logistics” are in discussion among members at the end of 2020.
(https://www.humanitarianresponse.info/operations/cambodia)
For more information on humanitarian agencies, please see the following link: 4.2 Humanitarian Agency Contact List.
1.2 Cambodia Regulatory Departments & Quality Control
General Department of Customs and Excise (GDCE)
Under the Ministry of Economy and Finance, the General Department of Customs and Excise (GDCE), as a member of the WCO since June 2011, has for mission to:
- facilitate International trade and protection of the national economy and trade
- collect and increase government revenues (duties, taxes, and other charges
- ensure fair economic competition, sustain economic development and viability of Cambodia
- enhance social safety and national security with prevention, surveillance and investigation of smuggling and other Customs offenses including drug trafficking and dumping of wastes etc.
- compile trade statistics, analyse trade patterns, and provide recommendations to policy makers.
Importers and Exporters must provide additional documentation and authorization for items that the Royal Government of Cambodia has determined to be sensitive or that are monitored for trade purposes. They are listed as Prohibited and Restricted Goods. The Enforcement of the List of Prohibited and Restricted Goods was revised with the Sub-decree No. 17/ANK/BK dated 26 February 2020, effective from 1 April 2020. https://customs.gov.kh/en
As part of government effort to enhance trade facilitation and serve the business community better, Cambodia has launched the National Trade Repository (NTR) in late 2015 as ‘the official source for all regulatory information relevant to traders who wish to import goods into Cambodia or export to other countries.’ Its website, hosted by the Ministry of Economy and Finance on behalf of all line Ministries and Institutions, provides public access to all necessary trade information, including customs permits and duties and trade regulatory procedures and documentation requirements among others. https://www.cambodiantr.gov.kh/
In the case where commodities have permission from the Council of Development for Cambodia (CDC), there shall be no need to request a permit from other competent ministries or institutions for import.
Council of Development for Cambodia (CDC)
The Council for the Development of Cambodia (CDC) is an executive agency of the Royal Government of Cambodia that serves as the “Etat-Major” and the “One-Stop Service” of the Royal Government responsible for the rehabilitation and development, public and private investments, and the establishment and management of special economic zones. In addition to reviewing applications for investment incentives, the mission of the CDC is to promote and facilitate foreign and local investments. http://www.cambodiainvestment.gov.kh/
Cambodian Rehabilitation and Development Board (CRDB)
The Cambodian Rehabilitation and Development Board (CRDB) is the “One-Stop Service” and the “Etat-Major” of the Royal Government that coordinates with development partners and NGOs who provide development assistance. CRDB also serves as a focal point in liaison with governmental institutions to manage development cooperation and partnerships in Cambodia. http://cdc-crdb.gov.kh/en/index.php
Ministry of Commerce (MOC)
The Ministry of Commerce’s (MOC) mission is to provide the public all trade-related services, diversify new markets, and continue implementing Cambodia’s trade policies for the great benefits of private sector development and Cambodian people’s interests. MOC undertook the formulation of its fourth- generation trade strategy called the Cambodia Trade Integration Strategy (CTIS) 2019-2023. http://www.moc.gov.kh/
Cambodia is a member of the World Trade Organisation (WTO) since 2004 https://www.wto.org/english/thewto_e/countries_e/cambodia_e.htm
On 09 March 2016 a joint declaration on “Setting formulas on retail price of gasoline in Cambodia” was signed by Ministry of Commerce, Ministry of Economy and Finance, and Ministry of Mines and Energy. The declaration contains 11 clauses. It allows each gas station to set its retail prices in accordance with fluctuations of the international market by applying the formula set out in the announcement. The 5th Clause stipulates that all retail gas stations, who sell gasoline products categorized regular or premium gasoline, must sell at a price not exceeding the price determined by the formula.
Consumer Protection, Competition, and Fraud Repression Directorate General (CCF formerly CAMCONTROL)
On 16 March 2020, the Royal Government of Cambodia adopted the Sub-Decree No. 38 ANKr. BK. on the Organization and Functioning of the Ministry of Commerce (abrogate Sub-Decree No. 131 ANKr. BK dated 2014) and upgraded CAMCONTROL to Directorate General (abrogate Sub-Decree No. 59 ANKr. BK dated 2008).
CAMCONTROL changed name to Directorate General of Consumer Protection, Competition and Fraud Repression (CCF). Its mandate is to research, organize and establish policy and strategic planning related to the quality and safety of products and services for the sake of ensuring consumer protection and fair market competition. The department cooperate with the relevant authorities to curb and crack down on counterfeit goods and take measures against abuse of dominant market position and curtail threats to competition. https://www.ccfdg.gov.kh/en/
The CCF is composed of 6 (six) departments: (i) Department of General Affaires and Public Relation; (ii) Department of Technical Affaires; (iii) Department of Consumer Protection; (iv) Department of Laboratories; (v) Department of Competition Affaires; and (vi) Department of HALAL affaires.
Ministry of Health (MOH)
MOH is the government ministry responsible for governing healthcare, the healthcare industry, public health and health-related NGOs in Cambodia. The Ministry governs and regulates the activity of medical professionals, hospitals and clinics in the country. www.moh.gov.kh
The Ministry of Health, as lead technical agency, is responsible for planning and oversight of the health sector response following COVID-19 and the Minister of Health chair the Inter-Ministerial Committee, along with Secretaries of State.
Department of Drugs and Food (DDF)
Under MOH, the department of Drugs and Food (DDF) performs as inspector and analyse all composition of drugs before allowing issuance of import permit. A certificate of analysis from this department is required by the General Department of Customs & Excise to import any drugs in Cambodia. https://www.ddfcambodia.com/.
Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry, and Fisheries (MAFF)
The Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries is delegated by the Royal Government to perform the guiding and administrative mission over the agricultural field of the Kingdom of Cambodia. https://web.maff.gov.kh/ The department of Plant Protection Sanitary and Phytosanitary (DPPSP) of MAFF is responsible of the implementation of plant quarantine under The Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries. As a member of WTO, Cambodia follow the rules laid down by the International Plant Protection Convention (IPPC) https://www.ippc.int/en/countries/cambodia/
Ministry of Industry, Science, Technology, and Innovation (MISTI)
In January 2020, the Ministry of Industry and Handicraft (MIH) changed name to the Ministry of Industry, Science, Technology and Innovation (MISTI). In the context of the Fourth Industrial Revolution, two new department have been created: The General Department of Science, Technology and Innovation and the National Institute of Science, Technology and Innovation (NISTI). https://www.misti.gov.kh/
Institute of Standards of Cambodia (ISC)
Under MISTI, the Institute of Standards of Cambodia (ISC) is the national standards body responsible for the preparation and publication of Cambodian standards and guidelines for products, commodities, materials, services and operations. All imported goods shall be compliant with Cambodia Industrial Standard and Quality & Safety Standard. of Cambodia. http://www.isc.gov.kh
Ministry of Mines and Energy (MME)
The Ministry of Mines and Energy (MME) prepare and implement policies, legal frameworks and regulations to govern the mining, oil and energy sectors in Cambodia since 2013. http://www.mme.gov.kh
The Electricity Authority of Cambodia (EAC) is an autonomous government agency created under the Electricity Law, responsible for regulating electricity services. It issues rules, regulations, and procedures; and provides monitoring, guidance, and coordination of operators in the energy sector—both suppliers and consumers—including requiring them to follow the policy, guidelines, and technical standards issued by the MME. The EAC as the regulator confirms whether the provision of services and the use of electricity are performed efficiently, qualitatively, sustainably, and in a transparent manner. All power service suppliers must be licensed by the EAC.
Electricité du Cambodge (EDC) is a state-owned and vertically integrated monopoly responsible for generation, transmission, and distribution. It is owned jointly by the MME and the Ministry of Economy and Finance. http://www.edc.com.kh/
Reference: https://www.adb.org/sites/default/files/linked-documents/50248-001-so.pdf
Ministry of Post and Telecommunication (MPTC)
The Ministry of Post and Telecommunication of Cambodia (MPTC) promote effective network infrastructure connectivity and accessible services of Post, Telecommunications, and ICT sectors across the Kingdom of Cambodia. https://www.mptc.gov.kh/
The General Department of Customs & Excise request for an approval letter from the Ministry of Post and Telecommunication to support any import permit request of telecommunication equipment.
Three Autonomous entities are under MPTC:
- Telecommunication Regulator Cambodia established in 2015 formulate the regulations, relating to the operation and provision of telecommunications network and services, in order to promote fair, efficient, and transparent competition in line with the Royal Government’s policy on the telecommunications sector. https://www.trc.gov.kh
- Telecom Cambodia, state-owned broad network telecom operator since 2005 http://www.tc.com.kh/
- Cambodia Post, offers postal services domestically and internationally in Cambodia https://www.cambodiapost.post/
Ministry of Public Works and Transport (MPWT)
The Ministry of Public Works and Transport (MPWT) https://www.mpwt.gov.kh/
- Prepare and monitor draft laws, guidelines and regulatory documents, National Policy and Strategic Plan of the Royal Government of Cambodia for the development of the Public Works and Transport sector, formulating master plan for land transport, railways, waterways, seas, seaports and logistics or other channels as allowed by the government.
- Plan, manage and disseminate technical regulations, standards and technologies to ensure and evaluate the construction and maintenance of roads, bridges, ports, railroads, rivers, seaside, ports, logistics and other related works related to public works and transport.
- Handle Cambodia transport system and promote online public service including: Vehicle Registration, Driving License and Motor Vehicle Control. MPWT also control the road vehicle weight limit, including taking strict enforcement measures to protect roads, bridges or other transport infrastructure.
- Develop human resources by encouraging research, technical research and the transfer of new technology for the development of the public transport sector.
As of March 1st, 2019, the former state Shipping Agency, Kampuchea Shipping Agency & Brokers (KAMSAB), was disbanded.
Secretariat of Civil Aviation (SSCA)
The Secretary of State of Civil Aviation was elevated to the rank of Minister in 2018 (Previously reporting to the Minister of Public Works and Transport). The secretariat has the responsibility for regulation of the civil aviation. Development of civil aviation activity and the civil aviation infrastructure, such as the nation’s airports and air traffic management system, has moved forward in Cambodia, particularly in the last 15 years. http://www.civilaviation.gov.kh/
Ministry of Interior (MOI)
The Ministry of Interior of Cambodia is responsible for public administration throughout Cambodia's 25 capital city-provinces and 203 district/Khan/Municipality. The Ministry governs the Cambodian National Police and the administration of the law enforcement; including the police academy, police training, judicial police, anti-drug efforts, border police and prison administration. https://www.interior.gov.kh/
1.3 Cambodia Customs Information
Duties and Tax Exemption
For contact information regarding government custom authorities, please follow the link: 4.1 Cambodia Government Contact List.
Emergency Response
Passed by Cambodia’s legislature in June 2015, Cambodia’s Disaster Management Law objective is to regulate disaster management in Cambodia. The article 31 of the law precise that all duties and taxes for the activities of the management of disaster and humanitarian respond which are provided to Cambodia shall be burden by the state.
|
Agreements / Conventions Description |
Ratified by Country? |
|---|---|
|
WCO (World Customs Organization) member |
Yes, dated 03 APR 01 |
|
Annex J-5 Revised Kyoto Convention |
Yes, dated 28 JUN 14 |
|
OCHA Model Agreement |
No |
|
Tampere Convention (on the Provision of Telecommunication Resources for Disaster Mitigation and Relief Operations) |
No |
|
Regional Agreements (on emergency/disaster response, but also customs unions, regional integration) |
The ASEAN Agreement on Disaster Management and Emergency Response (AADMER) https://ahacentre.org/wp-content/uploads/2016/11/AADMER-DOCUMENT.pdf |
Exemption Regular Regime (Non-Emergency Response)
The exemption or partial exemption of import duties and taxes are granted for certain goods and to certain qualified importers, referring to articles 26 & 27 under Chapter 4 of Customs Law, Prakas N. 105 MEF.BRK dated 15 February 2008.
The Customs Law, Article 26 states that: " goods for foreign diplomatic or consular missions, international organizations and agencies of technical co-operation of other governments, for use in the exercise of their official function and when so certified by the Head of Mission and by the Ministry of Foreign Affairs and International Cooperation".
More information can be found on the customs website in “Customs Procedures / Special Procedures Section” and for preferential treatment on duties and taxes and regional agreements please refer to Customs Website in the related section under Publication at https://customs.gov.kh
|
Organizational Requirements to obtain Duty Free Status |
|---|
|
United Nations Agencies |
|
International NGOs (INGOs) and UN agencies are registered at the Ministry of Foreign Affair and International Cooperation (MFA/IC) with whom they sign a Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) & Plan of Operation valid for 3 years. An MOU is also signed between the organization and each ministry involved in the activities performed. These documents contain more specific binding information on duties and taxes exemptions from the Ministry of Economics and Finance. The MOU and a master list are registered at the Council for Development of Cambodia (CDC). |
|
Non-Governmental Organizations |
|
Local NGOs register at the Ministry of Interior (MOI). They may benefit from duties and taxes exemption if applicable by law or if they have signed an MOU, with a line ministry involved in the activities performed, granting exemption. https://www.ccc-cambodia.org/en/about-us/faq |
Exemption Certificate Application Procedure
|
Duties and Taxes Exemption Application Procedure |
|
Generalities (include a list of necessary documentation) |
|
All imported goods whose duties and taxes are borne by the Royal Government are required to apply for Customs Permit at GDCE. In case of donation to any government agency or ministry, a letter of the agency/ministry to GDCE is required. If an MOU has been signed, the importers shall apply for duties & taxes exemption of each import through the Council for Development of Cambodia (CDC). Upon receiving the approval from CDC, a customs permit will be applied at the General Department of Customs & Excise (GDCE). Documents required to apply: Application letter for duty exemption, invoice, Packing list, B/L, CDC approval and master List (if applicable). |
|
Process to be followed (step by step or flowchart) |
|---|
|
Procedure at the General Department of Customs and Excise 1) Enter data into customs system name “Secretariat Support System” 2) Registration at front gate (hard copy) 3) GDCE Secretariat (hard copy) 4) GDCE stamping (hard copy) 5) Enter data into customs system name “National Single Window” 6) Printing customs declaration at customs Regime Department (hard copy) 7). Enter data into customs system name “ASYCUDA” |
Exemption Certificate Document Requirements
|
Duties and Taxes Exemption Certificate Document Requirements (by commodity) |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
Food |
NFI (Shelter, WASH, Education) |
Medicines |
Vehicles & Spare Parts |
Staff & Office Supplies |
Telecoms Equipment |
|
Invoice |
Original, 1 copy, applies to UN and NGOs |
Original, 1 copy, applies to UN and NGOs |
Original, 1 copy, applies to UN and NGOs |
Original, 1 copy, applies to UN and NGOs |
Original, 1 copy, applies to UN and NGOs |
Original, 1 copy, applies to UN and NGOs |
|
AWB/BL/Other Transport Documents |
Original, 3 copies, applies to UN and NGOs |
Original, 3 copies, applies to UN and NGOs |
Original, 3 copies, applies to UN and NGOs |
Original, 3 copies, applies to UN and NGOs |
Original, 3 copies, applies to UN and NGOs |
Original, 3 copies, applies to UN and NGOs |
|
Donation/Non-Commercial Certificates |
No |
No |
No |
No |
No |
No |
|
Packing Lists |
Original, 1 copy, applies to UN and NGOs |
Original, 1 copy, applies to UN and NGOs |
Original, 1 copy, applies to UN and NGOs |
Original, 1 copy, applies to UN and NGOs |
Original, 1 copy, applies to UN and NGOs |
Original, 1 copy, applies to UN and NGOs |
|
Other Documents |
Original, 1 copy, applies to UN and NGOs |
Original, 1 copy, applies to UN and NGOs |
Original, 1 copy, applies to UN and NGOs |
Original, 1 copy, applies to UN and NGOs |
Original, 1 copy, applies to UN and NGOs |
Original, 1 copy, applies to UN and NGOs |
|
Permits |
- |
- |
Need permission from MOH |
- |
- |
Need permission from MPTC |
|
Additional Notes |
||||||
|
Government of Cambodia requires to have certificate of analysis which is issued by the origin country for any importation of Red Food such as canned fish or vegetable oil, which shall be free from: 1. PARA RED 2. RHODAMINE B 3. SUDAN RED DYES (SUDAN I, II, III, and SUDAN IV) |
||||||
Customs Clearance
General Information
|
Customs Information |
|
|---|---|
|
Document Requirements |
The National Trade Repository (NTR) provides public access to all necessary trade information, including customs permits and duties and trade regulatory procedures and documentation requirements among others. https://www.cambodiantr.gov.kh/ Following Prakas No. 1447 MEF dated 26 December 2007, all exported or imported goods, whether or not exempt from duties and taxes must be subject to a customs declaration. The customs declaration form is a Single Administrative Document – SAD). Customs Broker/Declarant shall inputs information of SAD directly into the Automated System on Customs Data (ASYCUDA). http://www.customs.gov.kh/customs-declaration/ In January 2021, GDCE request all importers and exporters to complete their applications electronically through the “Secretariat Support System and National Single Window System” for all import and export cargoes. |
|
Embargoes |
None |
|
Prohibited Items |
Specific drugs, protected species, imitation and counterfeit materials, wine and spirits. (it is applying as per regulations prescribed in Sub-decree n. 209 ANK.BK dated 31 December 2007 |
|
General Restrictions |
GMO Commodities are not allowed into the country. it is applied as per regulations prescribed in Sub-decree N.209 ANK.BK dated 31 December 2007 Sub-decree No. 17/ANK/BK dated 26 February 2020, on the Enforcement of the List of Prohibited and Restricted Goods (Effective from April 1, 2020, onwards); More information on GDCE |
Customs Clearance Document Requirements
|
Customs Clearance Document Requirements (by commodity) |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
Food |
NFI (Shelter, WASH, Education) |
Medicines |
Vehicles & Spare Parts |
Staff & Office Supplies |
Telecoms Equipment |
|
D&T Exemption Certificate |
Yes, Original, 1 copy, applies to both UN and NGO |
Yes, Original, 1 copy, applies to both UN and NGO |
Yes, Original, 1 copy, applies to both UN and NGO |
Yes, Original, 1 copy, applies to both UN and NGO |
Yes, Original, 1 copy, applies to both UN and NGO |
Yes, Original, 1 copy, applies to both UN and NGO |
|
Invoice |
Yes, Original, 1 copy, applies to both UN and NGO |
Yes, Original, 1 copy, applies to both UN and NGO |
Yes, Original, 1 copy, applies to both UN and NGO |
Yes, Original, 1 copy, applies to both UN and NGO |
Yes, Original, 1 copy, applies to both UN and NGO |
Yes, Original, 1 copy, applies to both UN and NGO |
|
AWB/BL/Other Transport Documents |
Yes, Original, 1 copy, applies to both UN and NGO |
Yes, Original, 1 copy, applies to both UN and NGO |
Yes, Original, 1 copy, applies to both UN and NGO |
Yes, Original, 1 copy, applies to both UN and NGO |
Yes, Original, 1 copy, applies to both UN and NGO |
Yes, Original, 1 copy, applies to both UN and NGO |
|
Donation/Non-Commercial Certificates |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
|
Packing Lists |
Yes, Original, 1 copy, applies to both UN and NGO |
Yes, Original, 1 copy, applies to both UN and NGO |
Yes, Original, 1 copy, applies to both UN and NGO |
Yes, Original, 1 copy, applies to both UN and NGO |
Yes, Original, 1 copy, applies to both UN and NGO |
Yes, Original, 1 copy, applies to both UN and NGO |
|
Phytosanitary Certificate |
Yes, Original, 1 copy, applies to both UN and NGO |
Nil |
Yes, Original, 1 copy, applies to both UN and NGO |
Nil |
Nil |
Nil |
|
Other Documents |
n/a |
n/a |
Yes, if any |
n/a |
n/a |
Yes, If any |
|
Additional Notes |
||||||
|
- For narcotic drugs, medicines, a permit is required from the Ministry of Health http://moh.gov.kh/ - For live animals, wood products a permit is required from the Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and fishery https://web.maff.gov.kh/ - For firearms, permit is required from the Ministry of Interior https://www.interior.gov.kh/ - For subjects of culture and arts, a permit is required from the Ministry of Culture and Art. |
||||||
Temporary Import Regime
Certain articles can be temporarily imported to be re-exported and are exempt from import duties and taxes. The importers are required to pledge that such articles will be re-exported within a specified period and provide a guarantee which is refunded after all the obligations under the pledge have been fulfilled. Exemption of guarantee may be applied based on Importer.
To secure the exemption of Cambodian import duties and taxes on articles to be temporarily imported and re-exported after use for a defined period, the importers are required to apply for approval from the related Ministry, CDC or GDCE directly based on their registration status.
Based on the commodity, a processing Certificate from the Ministry of Industry, Science, Technology and Innovation (MISTI) may be required. The Certificate shall show an estimated usage rate for the materials. The materials are declared to Customs on arrival, and the finished products are declared on exportation.
Based on the temporary condition, a joint Committee comprised of representatives of the Ministry of Economy and Finance, CDC, GDCE and Tax Department, MISTI and Ministry of Commerce may verify that all temporarily imported materials have been satisfactorily accounted for by manufacture into exported products.
Instruction of temporary import must be indicated in all documents at time of import (invoice, packing list and bill of lading).
For additional information, please see the following documents: